3 Simple Ways To Improve Your Home Sound System
- Written by News Feature Team
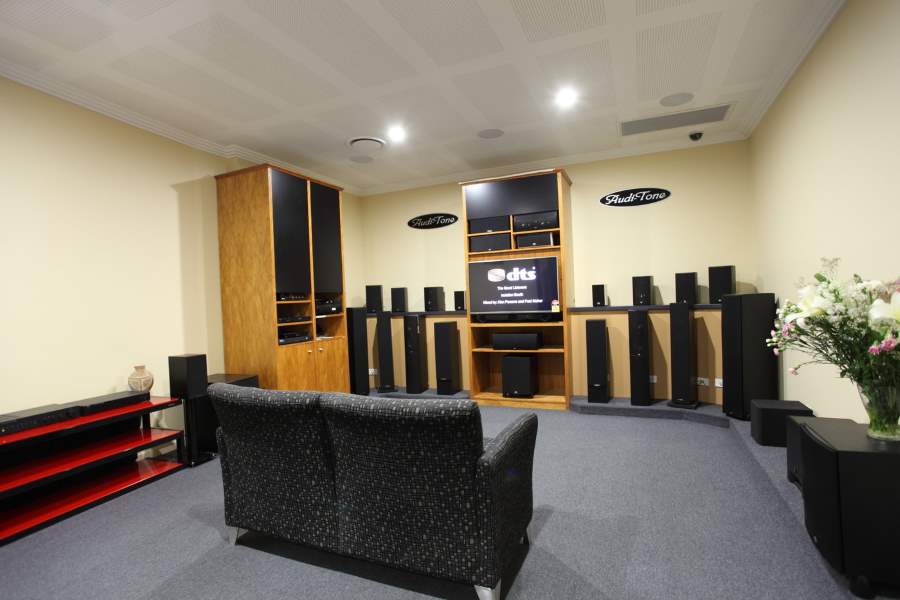

There’s a reason people watch movies more than once at the cinema when they first hit the big screen – and it’s not the popcorn. It’s the ambience of the theatre that really has you going back before your new favourite movie is relegated to DVD. The very same ambience you try to replicate in your home, a feat that has varying degrees of success. Below are a few simple ways to help turn your lounge into the new theatre.
1. Move It Around
Your home sound system isn’t bolted down; it’s moveable for a reason. Have a look through your movie collection or whip out your favourite video game, load it up and start sound testing. The aim of this is to adjust where your surround sound speakers are positioned to get maximum effect. Remember: sound bounces and there can be a lot of reverb, so this might take a lot of tweaking. Try angling your speakers for greater effect. A big mistake is to hide the bass unit away in the corner – let it do its job, and try it out in various locations until you find something that suits. Of course, if it turns out that your home sound system could do with an upgrade, you could always visit a website such as Graham Slee HiFi for some useful tips on how to improve the quality of your sound too!
2. Complement The Sound
If you want the true experience, the benefit of having a high-quality TV cannot be understated. The same applies to your current sound system. Don’t mix and match out-of-date pieces with newer, better models. Specialist companies such as Todds Hi Fi are perfect for keeping your entire home cinematic experience up to date. There’s also aesthetics to think about. Set your lounge or living room up in a way that’s inviting, because it’s much easier to enjoy the experience when you enjoy the space.
3. Watch Out For Your Surroundings
Even if you’ve got the best sound system in the world, it can be significantly downplayed by the smallest drawbacks. This one is obvious during the day but can easily be missed at night: make sure you draw the curtains. Glass can play havoc with sound reflection. Put simply, it can appear to be coming from two places at once – the TV and the glass. The easy fix for this is to keep the curtains closed. While you’re at it, make sure you turn out all the lights as well. It’s the small things that count when recreating that cinematic experience!
These changes will make an immediate difference and turn your home sound system into your own private theatre. All you’ll need to do is get comfortable and load up a movie or some good tunes!